BOYLE ' LAW
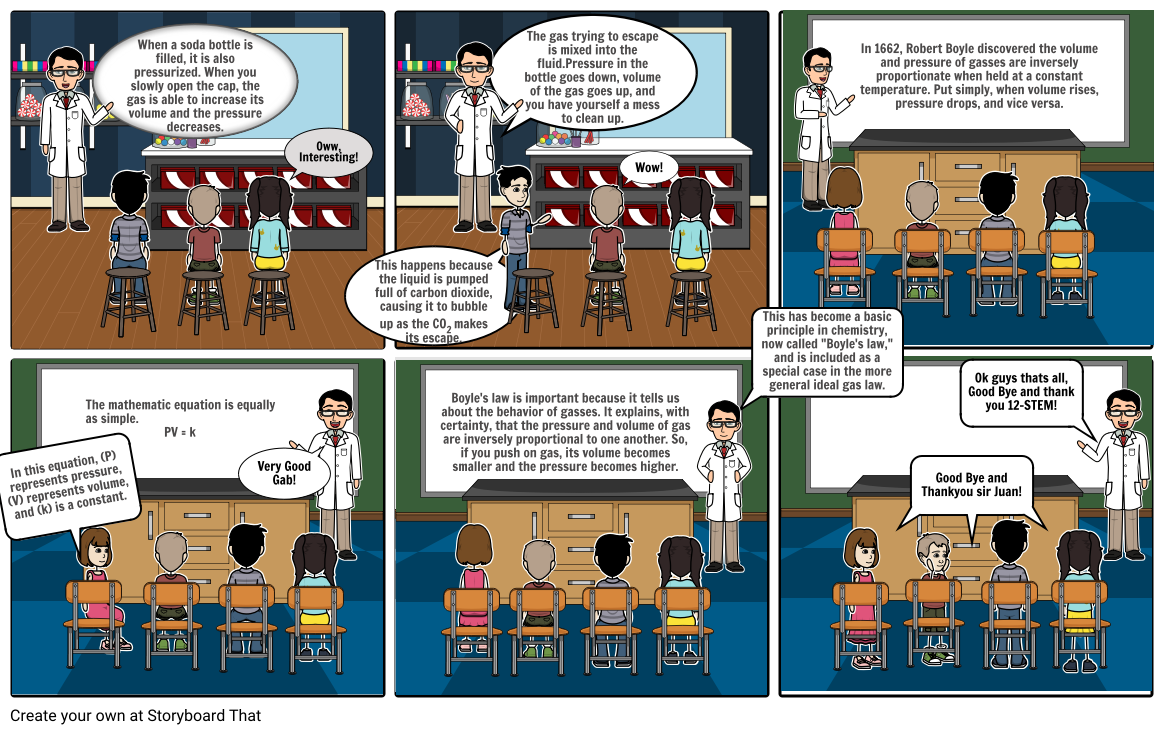
Boyle’s Law, an ideal gas law which states that the volume of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to its absolute pressure at a constant temperature. The law applies only to ideal gases which allow only pressure and volume to change.
In other words, the product of pressure and volume is constant for a fixed mass of ideal gas at fixed temperature.
The other way to express Boyle’s Law is as follows
Where
- P denotes pressure of the gas
- V denotes volume of the gas
- K is constant and holds units of force times and distance.

BOYLE ' S LAW FORMULA
According to this law, at a constant temperature, the product of pressure and volume is a constant:
PV = c
o
P ∝ 1/V
EXAMPLE FOR BOYLE ' S LAW PROBLEM
| Boyle's Law | |
| pressure at state 1 | |
| volume at state 1 | |
| pressure at state 2 | |
| volume at state 2 |
(1) A 1 L volume of a gas is at a pressure of 20 atm. A valve allows the gas to flow into a 12 L container, connecting the two containers. What is the final pressure of this gas?
A good place to start this problem is to write out the formula for Boyle's law and identify which variables you know and which remain to be found.
The formula is:
P1V1 = P2V2
You know:
Initial pressure P1 = 20 atm
Initial volume V1 = 1 L
final volume V2 = 1 L + 12 L = 13 L
final pressure P2 = variable to find
Initial volume V1 = 1 L
final volume V2 = 1 L + 12 L = 13 L
final pressure P2 = variable to find
P1V1 = P2V2
Dividing both sides of the equation by V2 gives you:
P1V1 / V2 = P2
Filling in the numbers:
(20 atm)(1 L)/(13 L) = final pressure
final pressure = 1.54 atm

GRAPH FOR THE BOYLE ' S LAW
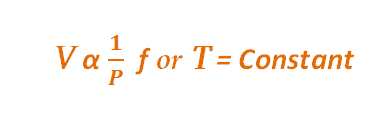
No comments:
Post a Comment